Research
2022/06 - now, eFMT-SLAM
The basic principle of FMT on image registeration.
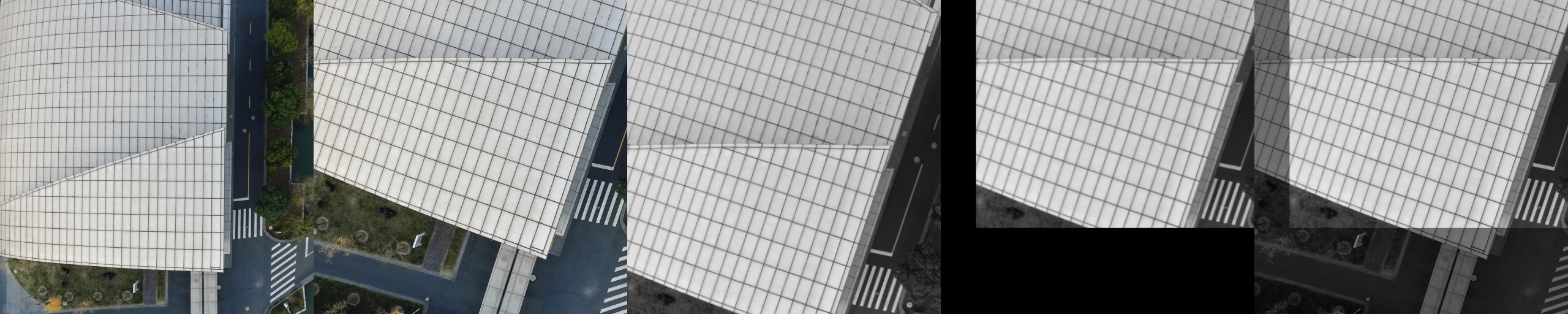 |
This image contains five single images. The first two are input images im0, im1. The third one is rotated im0 and the fourth is registered im0. We can find that these two images are registed very well from the last image.
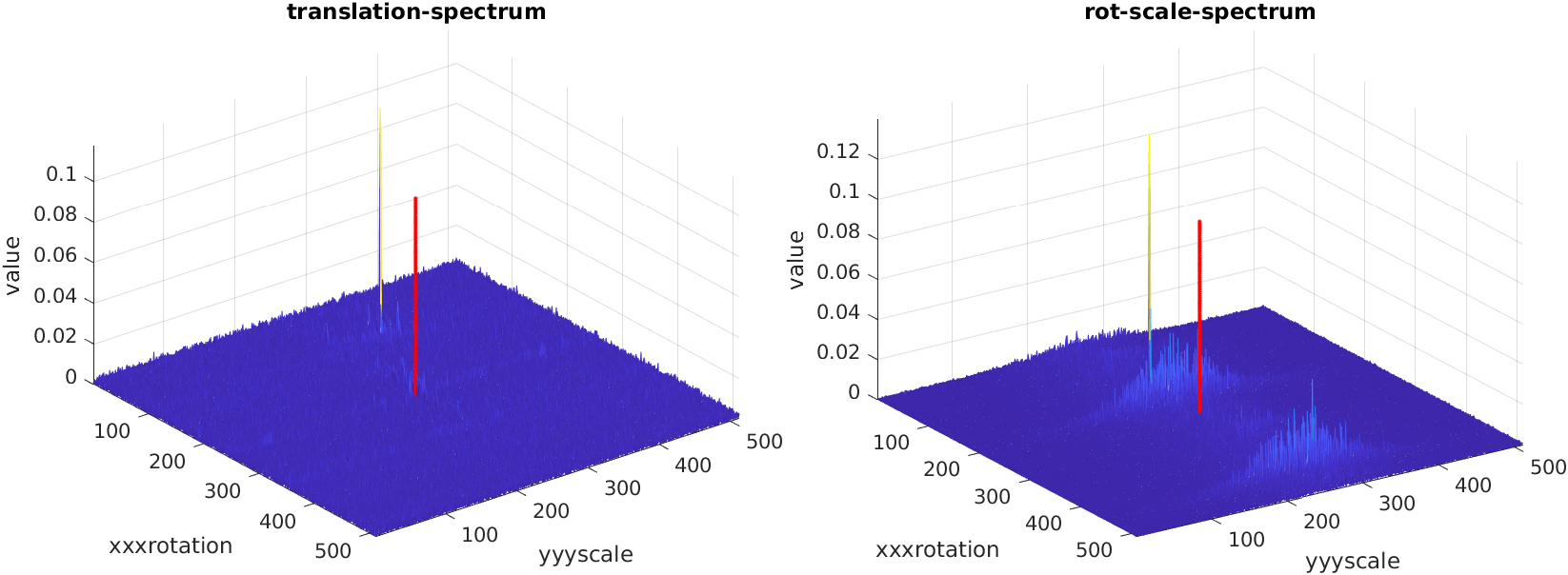 |
With the increasing application of intelligent mobile robots, stable and efficient Visual Odometry (VO) algorithms are becoming more and more important. Extended Fourier-Mellin Transform (eFMT) is a Fourier-Mellin Transform (FMT)-based image registration method that can be applied to top-down cameras, such as on aerial and underwater vehicles. eFMT extends FMT to multi-depth scenes, thus extending to more application scenarios. On this basis, we developed an optimized eFMT algorithm o-eFMT. We design and implement a pose estimation algorithm from several aspects. This algorithm first uses the Fourier Mellin Transform to convert the image to the frequency domain for processing, then extracts the scaling, rotation and translation transformations between images in two steps, and finally expresses the rotation and translation transformations in multi-depth scenes in the form of energy vectors. Through pattern matching, the scale of continuous pose estimation is unified. Furthermore, combination of the estimated pose with back-end optimization is used to optimize the loop closure of three consecutive frames, which improves the accuracy of the pose estimation.
The advantages of the algorithm in this thesis are: (1) use a new method to extract energy vectors, (2) improve the accuracy of pattern matching, (3) introduce a back-end optimization module, and thus reduce the error of camera pose estimation.
 |
Unlike the VO algorithm based on feature points, eFMT VO analyzes the representation of the image in the frequency
domain to extract the camera's motion transformation. And it is applied to consecutive images and the camera pose is
then estimated via the chain rule of the transforms. This project mainly focuses on the SLAM algorithm that is extended
by eFMT-based visual odometry(VO). It detects and closes loops in the path of the camera, and applies eFMT to two
non-consecutive but overlapping frames to furtherly constraining the pose of the camera.
2022/06 - 2022/07, Multi-cameras and IMU synchronization
In order to verify a developing SLAM method, we need to collect datasets with ground truth. We install 5 monocular cameras, 1 IMU and 1 GNNS receiver on the top of a car. The frequency of image messages is 40 Hz and IMU messages’ frequency is 400 Hz. But the GPS frame's frequency is only 10 Hz. These sensors have a pin for registering. Considering the IMU frequency is so high and it can publish a sample signal with low frequency, a proper way is to let IMU be the time source and trigger cameras and GNNS receiver. All sensors and launched with ros drivers and communicate with rostopic. Three computers connect all sensors and store the data by advertising topics.
2021/12 - 2022/04, Spotlights: Probing Shapes from Spherical Viewpoints
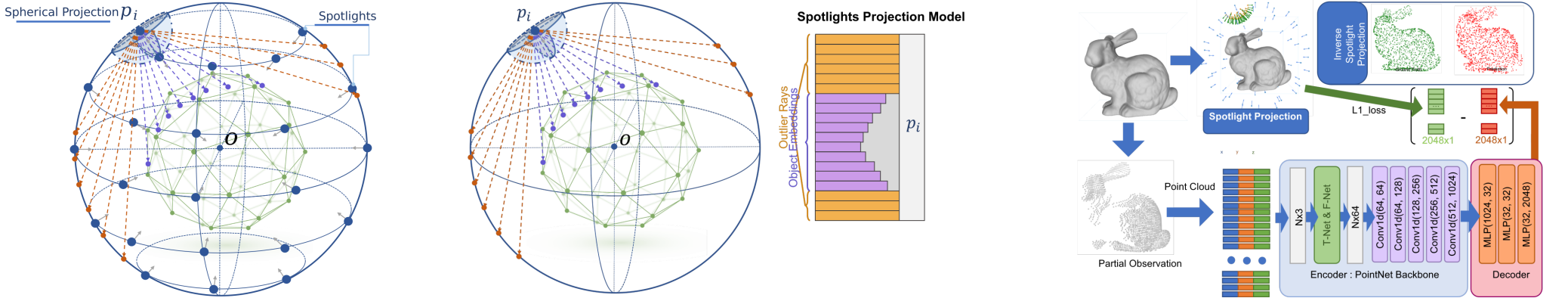 |
We have realized a new representation method of 3D objects based on the double sphere sampling model, and given the mathematical derivation and experimental verification. Our method are verfied on KITTI360 dataset and have a good performence.
This work has been received by 2022 ACCV under the title of “Spotlights: Probing Shapes from Spherical Viewpoints”.
2021/06 - 2021/09, Accurate calibration of multi-perspective cameras from a generalization of the hand-eye constraint
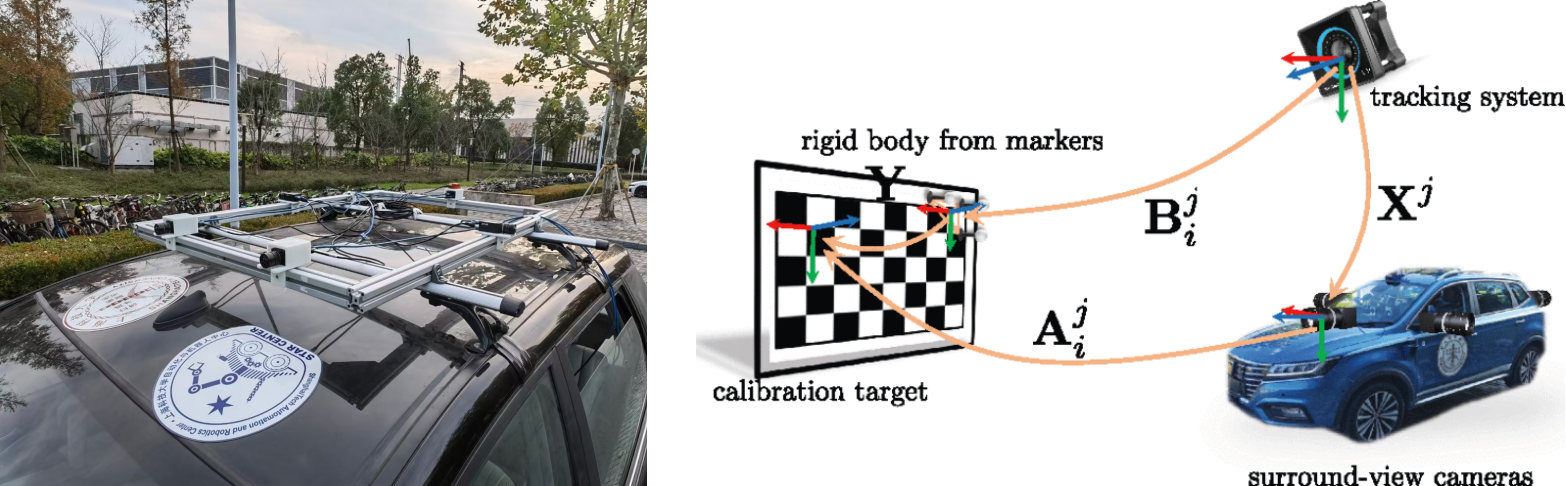 |
Large system size or absence of overlap in neighbouring fields-of-view often complicate their calibration.
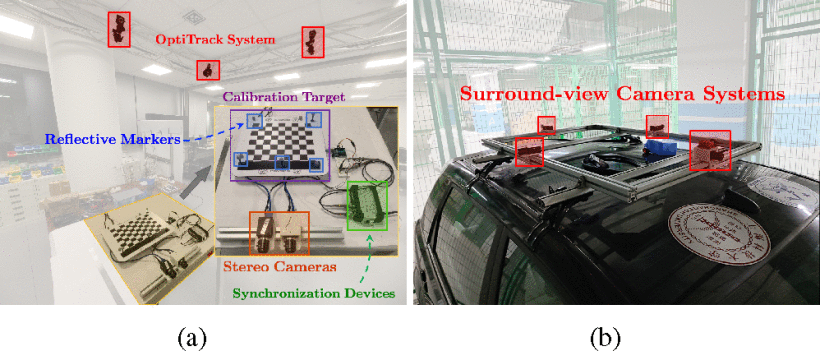 |
This project presents a novel solution that relies on the availability of an external motion capture system. Our core contribution consists of an extension to the hand-eye calibration problem which jointly solves multi-eye-to-base problems in closed form. We furthermore demonstrate its equivalence to the multi-eye-in-hand problem. The practical validity of our approach is supported by our experiments, indicating that the method is highly efficient and accurate, and outperforms existing closed-form alternatives.
2020/12, Laser-omni-sinusoid
After radar scans to obtain environmental information, the point cloud is projected onto a plane to form a picture. Use Fourier transform to analyze the transformation of pictures corresponding to consecutive frames, thereby inferring the camera's pose changes
2020/06, Undergraduate Thesis: Design of autonomous navigation mobile robot based on ROS
Validated SLAM algorithms such as gmapping, hector-slam and cartographer in gazebo and Rviz simulation environments, and was familiar with the complete autonomous navigation simulation experiment process.
2018 - 2022/01, Multi-robot localization method for time-varying pollution source in mechanical ventilation stable flow area
The national college students’ science and technology innovation project:
This project presented a particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm-based multi-robot olfaction method (UPSO) for locating time-varying contaminant sources in the indoor steady flow field with mechanical ventilation. For locating time-varying indoor particle sources under other ventilation modes, this study proposes the UWOA method based on Whale Optimization Algorithm.
Published an article in the journal “Building Science” titled “Experimental Research on Using Multiple Robots to Locate Indoor Periodic Pollution Sources”.